Products & Solutions
Stochastic Simulation
Stochastic Simulation
Monte Carlo methods are a widely used class of computational algorithms for simulating the behavior of various physical and mathematical systems. They are distinguished from other simulation methods (such as molecular dynamics) by being stochastic, that is nondeterministic in some manner - usually by using random numbers (or more often pseudo-random numbers) - as opposed to deterministic algorithms. Because of the repetition of algorithms and the large number of calculations involved, Monte Carlo is a method suited to calculation using a computer, utilizing many techniques of computer simulation.
A Monte Carlo algorithm is a numerical Monte Carlo method used to find solutions to mathematical problems (which may have many variables) that cannot easily be solved, for example, by integral calculus, or other numerical methods. For many types of problems, its efficiency relative to other numerical methods increases as the dimension of the problem increases.
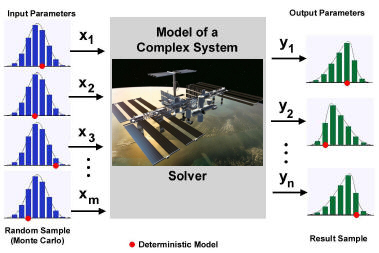
Applications
Monte Carlo methods are especially useful in studying systems with a large number of coupled degrees of freedom, such as liquids, disordered materials, and strongly coupled solids. More broadly, Monte Carlo methods are useful for modeling phenomena with significant uncertainty in inputs, such as the calculation of risk in business. A classic use is for the evaluation of definite integrals, particularly multidimensional integrals with complicated boundary conditions.
Monte Carlo methods are very important in computational physics and related applied fields, and have diverse applications from esoteric quantum chromodynamics calculations to designing heat shields and aerodynamic forms.
Monte Carlo methods have also proven efficient in solving coupled integral differential equations of radiation fields and energy transport, and thus these methods have been used in global illumination computations which produce photorealistic images of virtual 3D models, with applications in video games, architecture, design, computer generated films, special effects in cinema, business, economics and other fields.
Area of Expertise
- Stochastic modeling:
Stochastic modeling of operational environments, loads, material and structural behaviors
- Stochastic computation:
Deterministic and stochastic computational mechanics, stochastic finite elements, fluid dynamics, progressive failure mechanism